Glossary
The atmosphere is the layer of air that
surrounds the Earth. We live in the atmosphere and depend on it
to be able to breathe.
A barometer is an instrument that measures
the pressure of the atmosphere. One use of a barometer is to
help to forecast the weather.
A boiler is a vessel (or container) in
which water is boiled to make steam. While the water is
boiling, bubbles of steam form within it and rise to the
surface. The change from liquid water to steam is known as
evaporation.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
Condensation is what happens when a
substance changes from being a gas or vapour, like steam,
to a liquid like tap water. The
substance is said to condense. Whenever a substance condenses
it gives out heat. This is why hot steam can cause such a bad
burn if it comes in contact with our skin.
A condenser is a device that causes a vapour
to
condense back
to a liquid. A steam condenser is a vessel into which steam can
flow. The surfaces inside the condenser are kept cold by cold
water flowing through pipes that pass through the condenser.
The steam condenses on the cold surfaces and leaves as liquid
water.
A diesel engine is an oil-burning engine
that is commonly found in vehicles today. In the cylinders of a
diesel engine air is compressed to a high-pressure. The fuel
oil is then sprayed in and it burns immediately. The hot
combustion gases expand and push a piston down the cylinder.
The piston is connected to a crank to provide a rotary motion
output. Because the fuel is burned inside the cylinders, the
diesel engine is described as an internal combustion engine.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A diesel locomotive is a
vehicle that runs on tracks and is powered by a
diesel engine. The diesel engine burns fuel oil.
Diesel engines are commonly used in modern
locomotives. Diesel locomotives largely replaced
steam locomotives because they were more efficient.
The efficiency of an engine is
the amount of work produced for a given amount of
fuel energy used. An efficient engine would produce
a lot of work from a given amount of fuel. The
efficiency is usually written as a percentage (a
number divided by 100). Early steam engines had an
efficiency of perhaps 1%. Modern steam power plants
can have an efficiency of 40% or more.
Energy is the capacity to do
work: for example, to lift a mass of one kilogram
through a vertical distance of one metre. Almost
all the energy we use comes directly or indirectly
from the Sun. Energy from the Sun has been stored
in fuels such as coal or mineral oil.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A engine is a machine that can convert energy
into useful work.
Evaporation is what happens when a
substance such as water changes from being a liquid to a gas
(or
vapour). The
substance is said to evaporate. Steam is the common name for
water when it exists as a vapour. Whenever a substance
evaporates it takes in heat.
A flywheel is a heavy wheel that is used
to ensure smooth rotating motion. In a
reciprocating engine
a flywheel stores energy
over part of every revolution (or turn of
the engine's output shaft) and pays it back over the remaining
part of the revolution.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
‘Information Age’ is a name
for the times in which we live. Our society uses and
redistributes vast amounts of information, or data. This ranges
from details such a date of birth to visual information such as
a live football match transmitted by satellite television.
People can now find information that they need much more easily
than in the past.
Live steam is the steam at high pressure
and temperature that comes from the boiler of a steam power
plant.
A locomotive, or locomotive engine, is a
self-propelled vehicle that runs on tracks and is normally used
to pull a train consisting of many carriages or wagons.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A partial vacuum is a pressure that is
lower than the pressure of the atmosphere but greater than
zero.
The words ‘partial vacuum’ are
used to indicate that a vacuum is not a ‘perfect
vacuum’.
A perfect vacuum is a pressure of zero. In
other words, there is no pressure! The pressure in outer space
is nearly a perfect vacuum.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A petrol engine is a petrol-burning engine
that is commonly found in vehicles today. In a petrol engine,
petrol is mixed with air and the mixture flows into the
engine’s cylinders. In each cylinder the petrol-air
mixture is compressed and then ignited by an electric spark.
The hot combustion gases expand and push a piston down the
cylinder. The piston is connected to a crank to provide a
rotary motion output. Because the fuel is burned inside the
cylinders, the petrol engine is described as an internal
combustion engine.
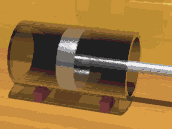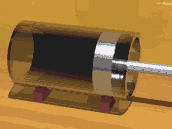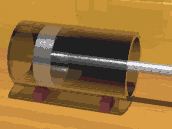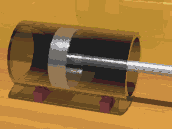
Demonstration of a reciprocating piston in a glass cylinder
A piston is a disc or cylinder that slides
back and forth within a hollow cylinder. As the piston is a
close fit within the cylinder, it blocks the escape of any gas.
In a steam engine the steam within a cylinder pushes against a
piston, causing it to move.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
Pressure is a measure of how hard an area
is being pressed. For example, the atmosphere presses down on
the Earth’s surface.
The pressure of the atmosphere is
equivalent to a weight of ten tonnes pressing down on every
square metre.
This pressure is because of the weight of
the air.
A reciprocating engine
is an engine in which one or more pistons
move back and forth within one or more cylinders.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A sauna is a room filled with hot steam.
People use a sauna to take a steam bath for health or
relaxation. In a sauna there is always air mixed with the steam
— otherwise it would not be possible to breathe.
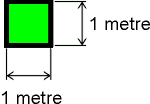
Explanation of Pressure (which refers to a square metre)
The ‘Steam Age’ is the name
for the period of history in which steam engines were widely
used to provide power for industry and transportation.
A steam engine is a machine that can do
useful work by using the energy of steam. Steam engines have
greatly influenced the world we live in.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A steam locomotive is a vehicle that runs
on tracks and is powered by a steam
engine. Solid fuel (such as
coal or wood) is burnt in a firebox to heat water in a boiler
and produce the steam. Steam locomotives
allowed railways to be opened up around the developing world.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A steam power plant is a complete system
for producing power (usually electric power). It consists of a boiler,
a turbine
connected to an electric generator, a
condenser
and a feed pump to return the condensed
water to the boiler. An electricity generating station may
contain a number of steam power plants.
Launcher and straw rocket
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story
A turbine is a machine that spins around
when a liquid or gas passes through it. It is a means of using
the energy of the liquid or gas to provide useful work.
A windmill is an example of a ‘wind
turbine’. In the past, windmills provided the work for
grinding wheat to make flour.
A vacuum is a pressure
that is lower than the pressure of the
atmosphere.
Because the Earth is surrounded by the
atmosphere, air will push its way into any empty space, if it
can find a way in. One way to create a vacuum is to pump air
out of a sealed container.
A valve is a device that allows the flow
of a liquid or gas to be shut off. Many valves are operated by
hand, just like a water tap.
A vapour is a gas that can turn to liquid
if it is cooled.
Use the Back button of your browser to return
to the story